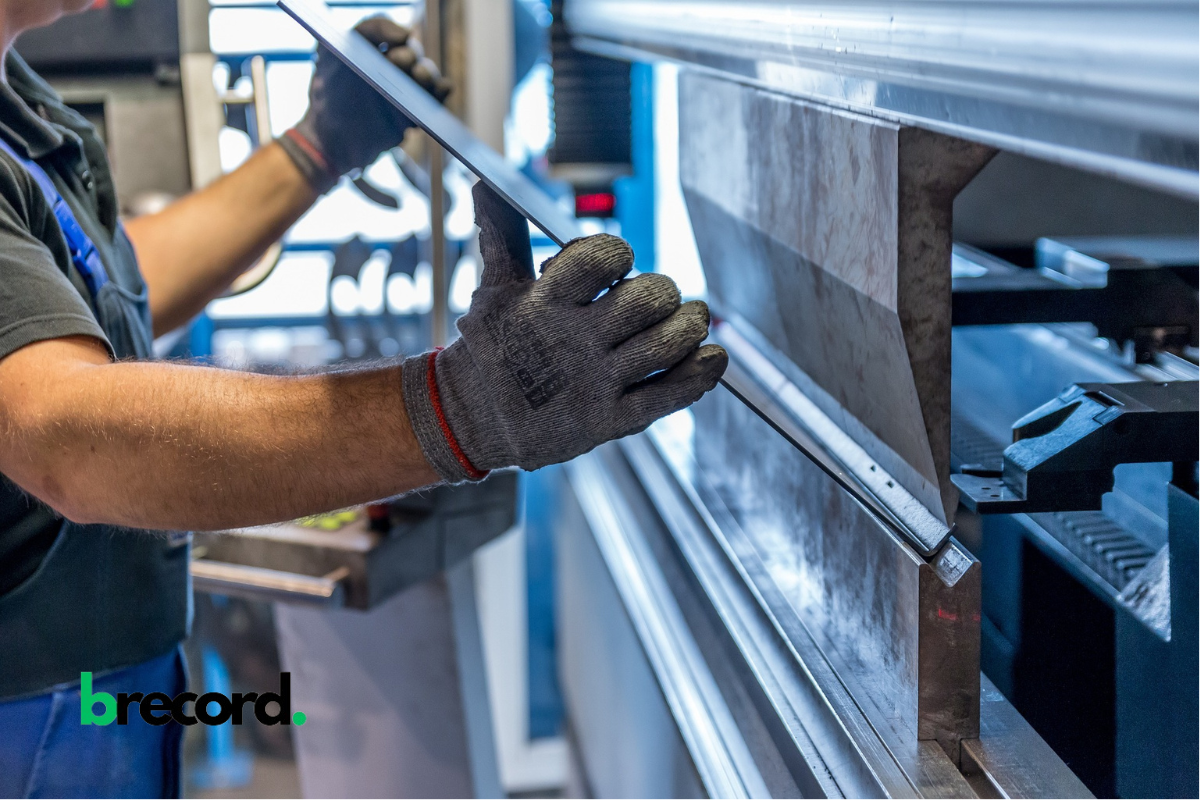
Cutting oil or lubrication plays a vital role in CNC machining services, ensuring the smooth and efficient operation of cutting tools and machinery. These fluids, called coolants, help reduce friction, heat and wear during machining. Therefore, the proper application of cutting oil for lubrication helps to ensure an improved machining operation.
This article explores the importance, types, and functions of cutting oil and lubrication in CNC machining.
What is Cutting Oil or Lubrication in CNC?
Cutting oil or lubrication is a crucial element in CNC machining services. Lubrication during machining helps to enhance the cutting process and ensure optimal performance and longevity of the tools and machinery. These fluids, sometimes called coolants or cutting fluids, are specifically designed to reduce friction, heat, and wear during machining.
During machining operations, particularly when cutting hard materials or running high-speed cutting, there is a high potential for heat build-up, which could affect the process. Continued machining at high temperatures may result in overheating and increased tool wear. Moreover, poor or inadequate use of cutting oil or lubrication may cause potential machining defects such as warping, distortion, burning, poor finishing, etc.
Types of Cutting Oil and Lubrication for Machining Services
Cutting fluids come in different forms and perform similar functions to improve the quality of the machining process.
- Mineral Oils: These are petroleum-based oils that offer good lubricity and cooling properties. They are often used for general-purpose machining tasks.
- Synthetic Fluids: As the name suggests, they are made from chemical compounds. However, like mineral oils, they provide excellent cooling and lubricating properties. They are ideal for high-speed machining and applications requiring high precision.
- Semi-Synthetic Fluids: These fluids blend mineral oils and synthetic compounds, offering a balance of lubricity, cooling, and cost-effectiveness.
- Water-Soluble Fluids: These fluids are diluted with water to form emulsions, which provide good cooling properties and reduce heat buildup during machining.
How Does Cutting Oil or Lubrication Improve CNC Machining Operations?
Applying cutting oil or lubrication during machining operations helps improve the cutting tool’s performance, allowing for more efficient machining. These cutting fluids improve machining operations in the following ways.
Increased Productivity
With adequate lubrication using appropriate cutting fluids, CNC machines can operate at higher speeds and feeds without compromising tool life or part quality. Cutting oils and lubrication enable smoother contact between the cutting tools and the workpiece, allowing for easier and more efficient cutting. In addition, the cutting fluids enable the machines to run at optimal performance levels, increase productivity, and reduce cycle times.
Cooling
Cutting oil acts as a CNC coolant, absorbing and dissipating the heat generated during machining. Adequate cooling is crucial for maintaining the integrity of the tool and the workpiece. Cutting oils and lubrication prevent the excessive build-up of heat, which can cause thermal deformation of the workpiece and reduce tool hardness. Moreover, by maintaining a stable temperature, cutting oil helps ensure that the dimensions and tolerances of the machined parts remain accurate.
Minimizing Build-Up Edge
Build-up edge (BUE) occurs when material adheres to the cutting edge of the tool, negatively affecting cutting performance and surface finish. Cutting oil and lubrication are effective in preventing BUE. Proper lubrication prevents material from sticking to the tool, ensuring smoother and more efficient cutting. Therefore, even as it prevents BUE, the application of cutting fluids may prove effective for achieving a more imported surface finish of the machined parts.
Facilitating High-Speed Machining
Since cutting oil and lubrication help to effectively manage heat and friction, machinists can explore high-speed machining operations. Effective cooling and lubrication allow higher cutting speeds without compromising tool life or part quality.
Therefore, machinists and OEMs can deliver high-quality CNC machined parts with high speed, which may be effective for meeting tight schedules and serve as a competitive edge in the market. In addition, high-speed machining increases production rates, making operations more efficient and cost-effective.
Enhancing Tool Performance
Cutting oil enhances the overall performance of cutting tools, particularly the cutting edge, by maintaining their sharpness and reducing wear. Adequate lubrication ensures that tools operate consistently, maintaining cutting efficiency and accuracy. Moreover, cutting fluids reduces the tool wear rate by minimizing friction and heat, which is critical for maintaining high-quality machining operations.
What is the Function of Cutting Oil or Lubrication?
We have mentioned some benefits of cutting oil or lubrication during CNC machining operations. Below, we explore in detail how these fluids can improve CNC machining.
Reduction of Friction and Wear
The primary function of cutting oil or lubrication is to reduce friction between the cutting tool and the workpiece. However, reducing friction during machining has other advantages. For example, friction leads to heat generation during machining and influences the surface finishing of the part.
Therefore, reducing friction helps create a cooling effect, modulating heat build-up. It also helps smoothen the cutting action, ensuring that the cutters move smoothly across the material, resulting in more precise cuts and improved surface finishing. With reduced friction, there is less potential for wearing of the cutting edges and teeth, ensuring that the tools last longer and maintain their sharpness, reducing the need for frequent replacements and maintenance.
Effective Heat Dissipation
CNC machining generates significant heat due to the high speeds and intense forces involved in cutting operations. Cutting oil aids in cooling, preventing overheating, and maintaining the dimensional accuracy of the cutting process. The coolant properties of cutting fluids help dissipate heat away from the cutting zone, preventing the workpiece and tool from overheating.
In addition, the cutting fluids reduce thermal expansion and contraction due to controlled temperature, ensuring that the machined parts maintain their precise dimensions and tolerances.
Enhanced Surface Finishing
The application of cutting oil directly impacts the quality of the machined surface. Cutting fluids create a lubricating layer that reduces the formation of burrs and rough edges, leading to a smoother and more aesthetically pleasing surface. Moreover, since lubrication increases the smoothness at which the cutting tools interact with the workpiece, it minimizes the risk of tool marks and scratches on the workpiece, enhancing the overall quality of the final product.
Efficient Chip Removal
During CNC machining, material removal generates chips that need to be efficiently managed to avoid disruptions. Cutting oils help flush away chips from the cutting area, preventing re-cutting, which can damage the workpiece. Also, lubrication reduces the risk of chips welding onto the tool, which can cause tool breakage and poor surface quality.
Corrosion Prevention
Some cutting fluids contain additives that protect the tool and workpiece from corrosion. These oils form a protective film over the machined parts and tools, preventing oxidation and rust, which is especially important for metals prone to corrosion.
Cost Efficiency
While cutting oil and lubrication doesn’t necessarily save costs, some of their advantages to machining operations are cost-saving. For example, they help extend the lifespan of cutting tools. Therefore, they reduce the need for frequent maintenance and tool replacements, which may be cost-intensive. In addition, they improve tool performance and reduce machine breakdowns, translating to less downtime and higher operational efficiency.
Conclusion
We have already discussed the types, importance, and functions of cutting oil and lubrication in CNC machining. The primary function of lubrication and applying cutting oil during machining is to reduce friction, which translates to other benefits it provides. Understanding the role of cutting oil and lubrication will allow machinists is essential to maximize these agents, contributing to better machining outcomes.
FAQs
What is the Difference Between Cutting Oil and Lubrication?
Cutting oil refers to fluids that reduce friction and heat during machining. On the other hand, lubrication includes a broader range of substances, including semi-solids and solid lubricants, used to reduce friction during machining.
Why is Cutting Oil Important in CNC Machining?
Cutting oil is crucial in CNC machining as it helps reduce friction, dissipate heat, prevent tool wear, and improve the surface finish of machined parts, ensuring high-quality production and extended tool life.
How Often Should Cutting Fluids Be Replaced in CNC Machining?
The frequency of cutting oil replacement depends on the machining operation type, the machining material, and the specific cutting oil used. Regular monitoring and maintenance are essential to ensure optimal performance.
Which is Better for CNC Machining: Cutting Oil or Lubrication?
The choice between cutting oil and lubrication depends on the specific machining requirements, materials, and operational conditions. Both have unique advantages; selecting the appropriate fluid is essential for optimal machining performance.
Check out our blog for more interesting reads.